A week ago, my father deleted an entire folder full of important work documents. He promptly managed to recover about 95% of them from backups, but the remaining 5% (the most recent and important ones) were not backed up. If you’re facing a similar situation and are wondering how to recover a deleted folder from your desktop or any other location, then you’re in the right place because this article describes the same methods I’ve successfully used to recover my father’s missing work documents.
What to Do If You Accidentally Delete an Entire Folder
When you discover that you’ve accidentally deleted an entire folder, there are certain actions you should perform immediately and some you need to avoid to maximize your chances of successful recovery:
✅ DO:
- ⏪ Try the Ctrl + Z shortcut. Windows maintains a history of recent actions, and the universal “undo” command works for file operations just as it does for text editing. If you’ve, for example, very recently deleted a folder in File Explorer, then here’s how to undo the deleted folder: open the File Explorer window, navigate to the location where the deletion took place, and press Ctrl+Z. Hopefully, the folder will instantly reappear. If not, move to the next bullet point.
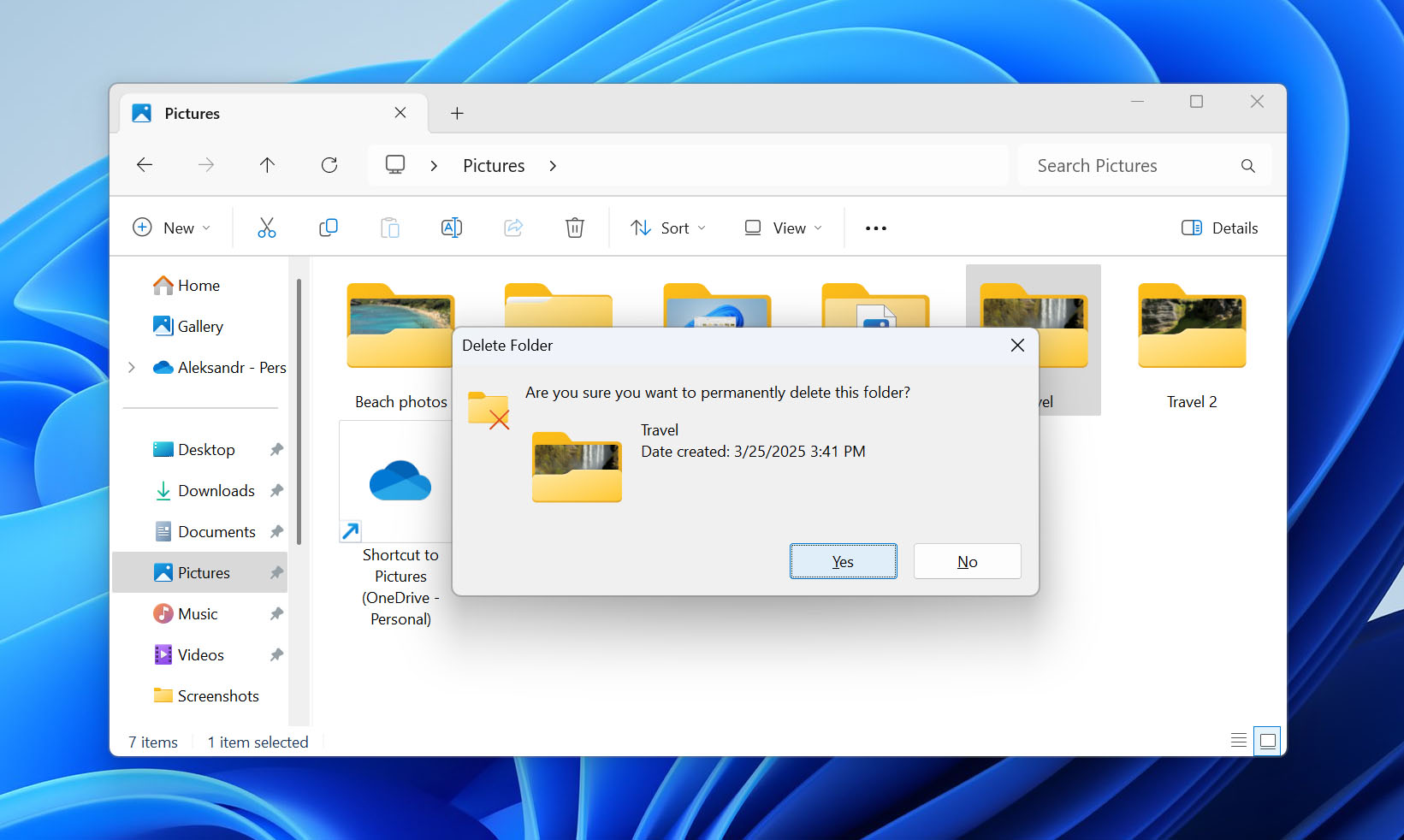
- 🗑️ Check the Recycle Bin. In many situations (see the next section for a detailed explanation), deleted folders are moved to the Recycle Bin. To check if your folder is in the Recycle Bin, simply double-click the Recycle Bin icon on your desktop, look for your folder, right-click it, and select Restore to return it to its original location.
- 🛑 Stop using the drive right away. If you can’t find the deleted folder in the Recycle Bin, then it’s really permanently deleted. The good news is that it’s possible to recover permanently deleted folders, but you must stop writing new data to the drive where the deleted folder was located otherwise you might overwrite the deleted data that still (hopefully) remains physically on the drive and make recovery impossible.
❌ DON’T
- 🧑💻 Don’t install data recovery software on the affected drive. Never install recovery software on the same drive where your deleted folder was located. Doing so could overwrite the very data you’re trying to recover. Instead, install the software on a different drive (like drive D: if your deleted folder was on drive C:).
- 🗂️ Don’t defragment the drive. As explained by HP, the purpose of defragmentation is to optimize the placement of data on a storage device for better performance. During defragmentation, files are moved to optimal physical locations, and the data originally stored in these locations may be overwritten in the process. Since modern versions of Windows (10 and 11) have automatic defragmentation scheduled by default, you should temporarily disable this feature by typing “Defragment and Optimize Drives” in the search bar, opening the utility, and turning off scheduled optimization until you’ve recovered your files.
Where Do Deleted Folders Go in Windows
I know that you’re anxious to learn how to recover a deleted folder, but taking another minute or two to understand where deleted folders go in Windows can greatly help you find and recover them. Contrary to what many users believe, “deleted” doesn’t always mean “gone forever.”
When you delete a folder using the Delete key or right-click and select “Delete,” the operating typically system moves it to the Recycle Bin, which acts as a temporary storage area for deleted items. The word “typically” is important because there are several situations where deleted folders don’t end up in the Recycle Bin:
- Size limitation: The Recycle Bin has a maximum storage capacity (typically 5-10% of your drive space). If your deleted folder exceeds this limit, Windows will bypass the Recycle Bin entirely and permanently delete the folder.
- Shift+Delete: If you hold the Shift key while deleting a folder to perform what’s commonly called Shift-deletion, you’re explicitly telling Windows to skip the Recycle Bin and delete the folder permanently.
- External drives: Folders deleted from SD cards and USB flash drives bypass the Recycle Bin and are deleted permanently. However, folders deleted from external hard drives and SSDs usually do go to the Recycle Bin (provided they’re formatted with NTFS or FAT32 file systems).
- Command Prompt deletions: Folders deleted using Command Prompt commands bypass the Recycle Bin and are deleted permanently.
When a folder is permanently deleted (either via Shift+Delete, Recycle Bin emptying, or bypassing the Recycle Bin due to size limitations), Windows removes the file system’s reference to that folder but doesn’t immediately erase the actual data from your drive.
The physical data remains on your drive until that space is needed for new files and gets overwritten. This is why it’s possible to recover permanently deleted folders using data recovery software, which is exactly what the next section of this article is dedicated to.
How to Recover a Deleted Folder on Windows Computer
By now, you’ve likely checked your Recycle Bin and discovered your folder isn’t there. Perhaps you used Shift+Delete, exceeded the Recycle Bin’s size limit, or deleted the folder from an external device. Maybe you emptied the Recycle Bin without realizing your important folder was inside. If so, then your next step should be to use data recovery software for Windows.
Method 1: Use Data Recovery Software for Windows
Data recovery software for Windows can retrieve deleted folders from all kinds of storage devices, such as internal hard drives, external USB flash drives, and memory cards, by analyzing them directly
What’s especially useful when recovering permanently deleted folders is the fact that Disk Drill is able to recover data with the original folder structure and file names using its two-stage recovery approach.
First, Disk Drill searches for folders using file system pointers that might still exist after deletion. If it’s unable to find your folder using these pointers, it then performs a signature scan, which can find individual files from your deleted folder based on their unique file signatures even when the folder structure itself is no longer detectable.
Sounds complicated? It technically is, but Disk Drill hides all the complexity behind its intuitive interface that boils down the recovery process into a few simple steps.
To recover permanently deleted folders:
- Download Disk Drill for Windows and install it. Always download and install data recovery software on a different drive than the one containing your deleted folder. Installing software on the same drive could overwrite your deleted data and make recovery impossible.

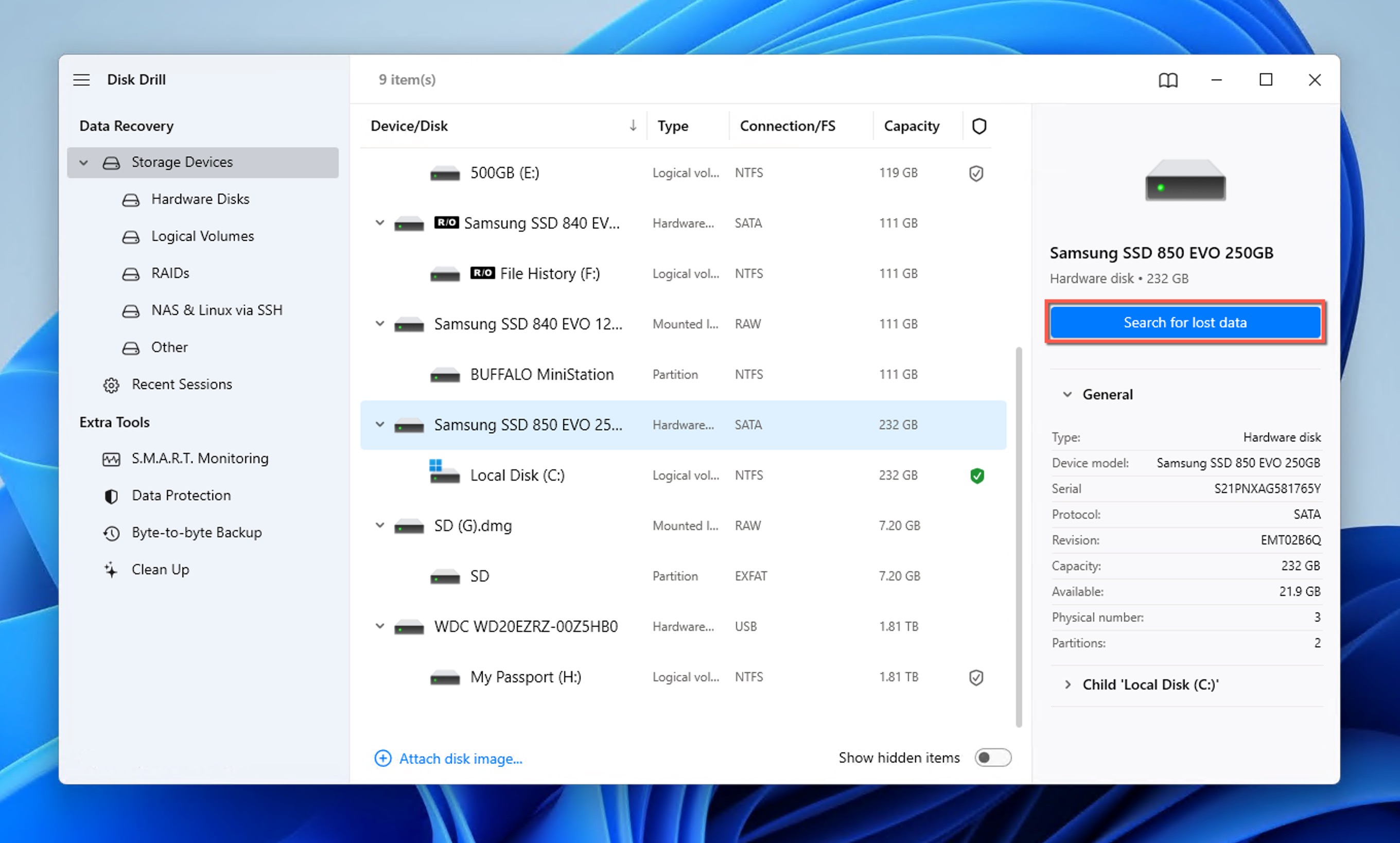
- Launch Disk Drill for Windows and click the Search for lost data button next to the hard drive where your lost folder was located.
- Wait for Disk Drill to find all recoverable files. The software automatically combines multiple scanning methods to maximize your chances of recovery, and it displays detailed information about its progress so that you can always see how many files have been found and how much time the scan will approximately take.
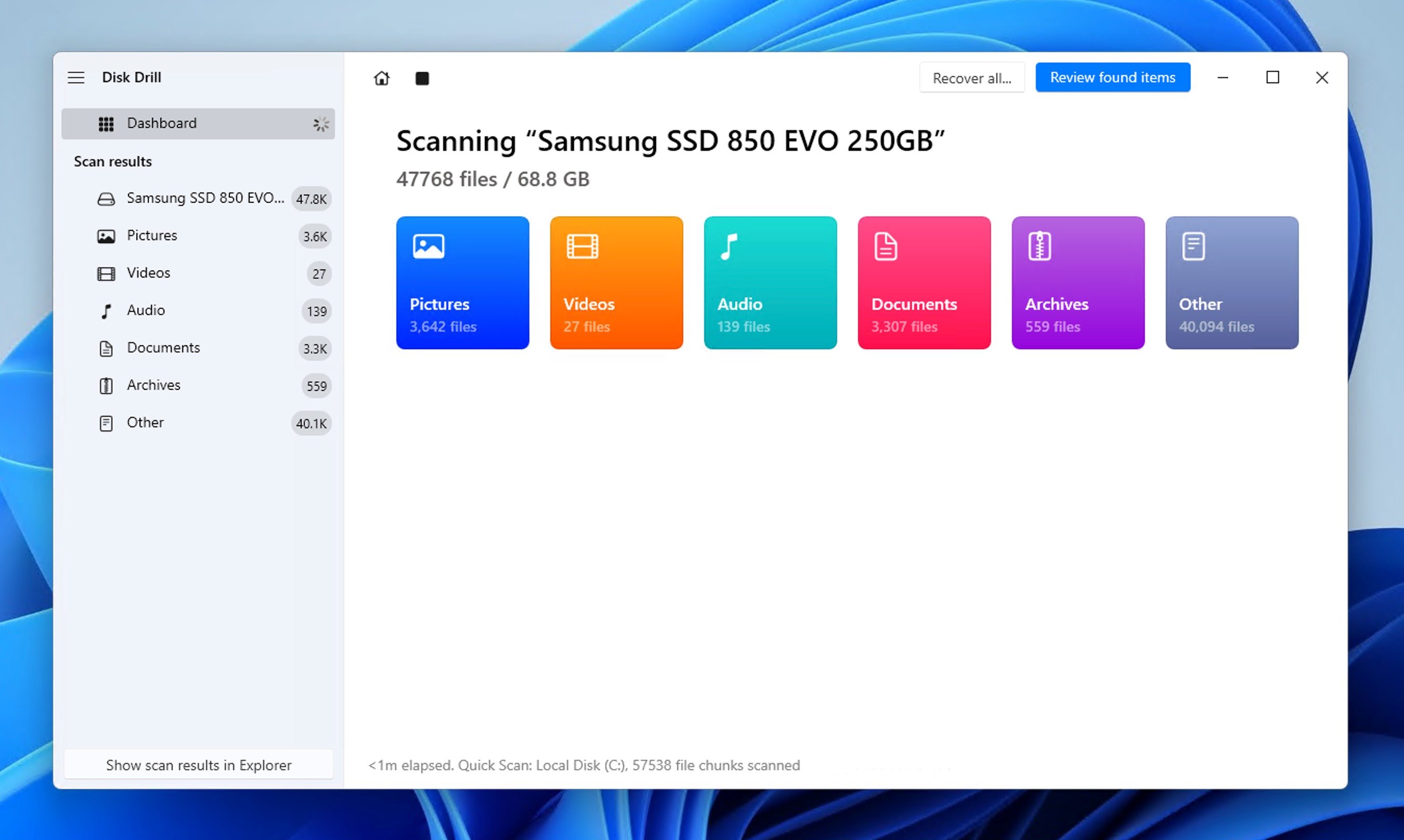
- Select which files you want to recover. You can either recover entire folders or select specific files. Additionally, you can sort the results in a number of different ways and even enable file type filters, which can greatly help if you’re looking for specific file types, such as Word documents or pictures.
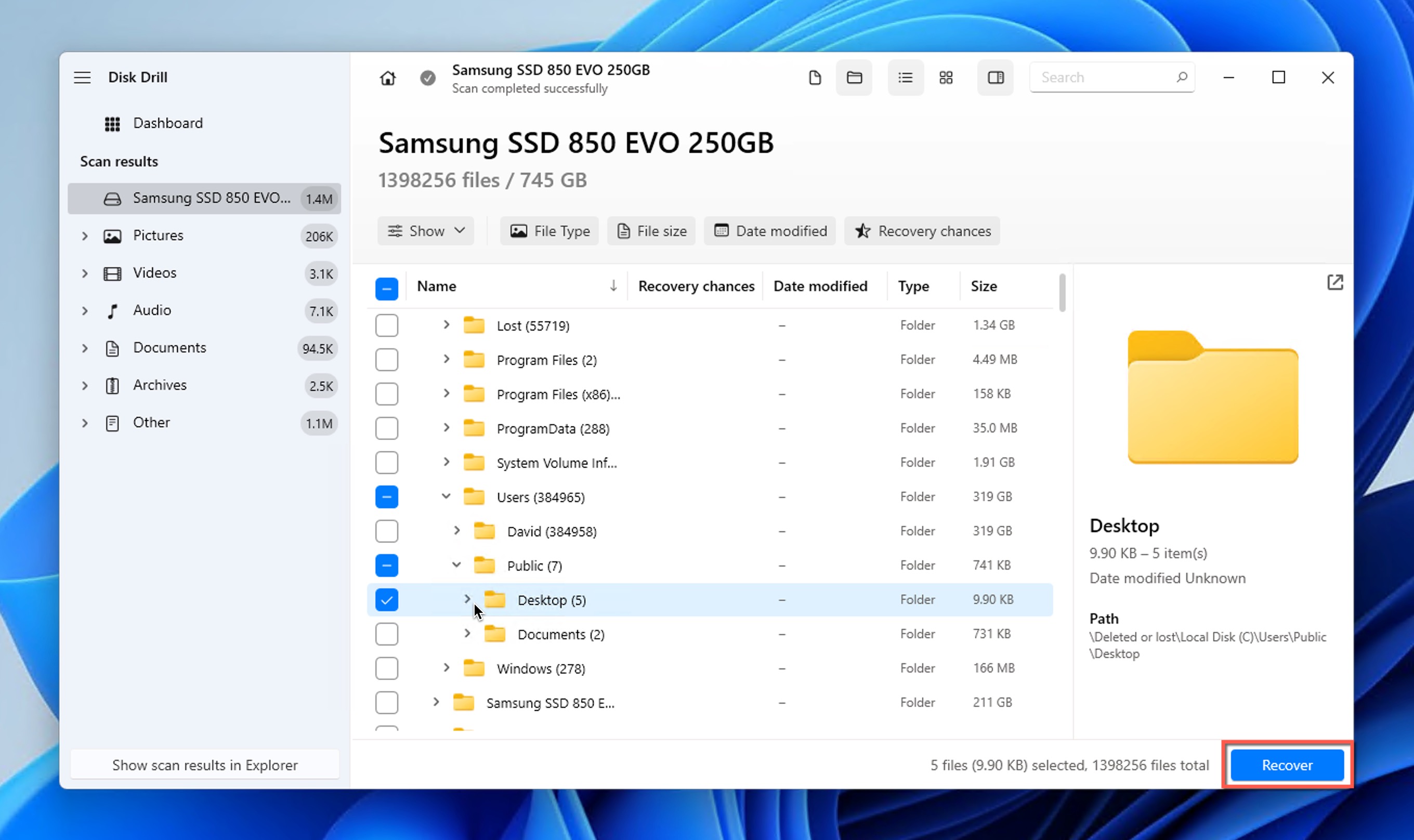
- Begin the recovery process by clicking the Recover button. You will be asked to choose a suitable recovery directory. Again, pick a location on a different storage device than the one where the deleted folder was located
Method 2: Use the File History Feature
If you’ve enabled Windows’ built-in backup tool, called File History, you may be able to retrieve a deleted folder without using third-party software.
When enabled, File History automatically backs up all your libraries (folders like Documents, Music, Pictures, Videos, and Desktop), so any sub-folder deleted from these locations should be backed up.
I personally like to access my File History backups through the classic Control Panel:
- Click on the Windows Start menu and type “Control Panel” in the search box.
- Open the Control Panel from the search results.

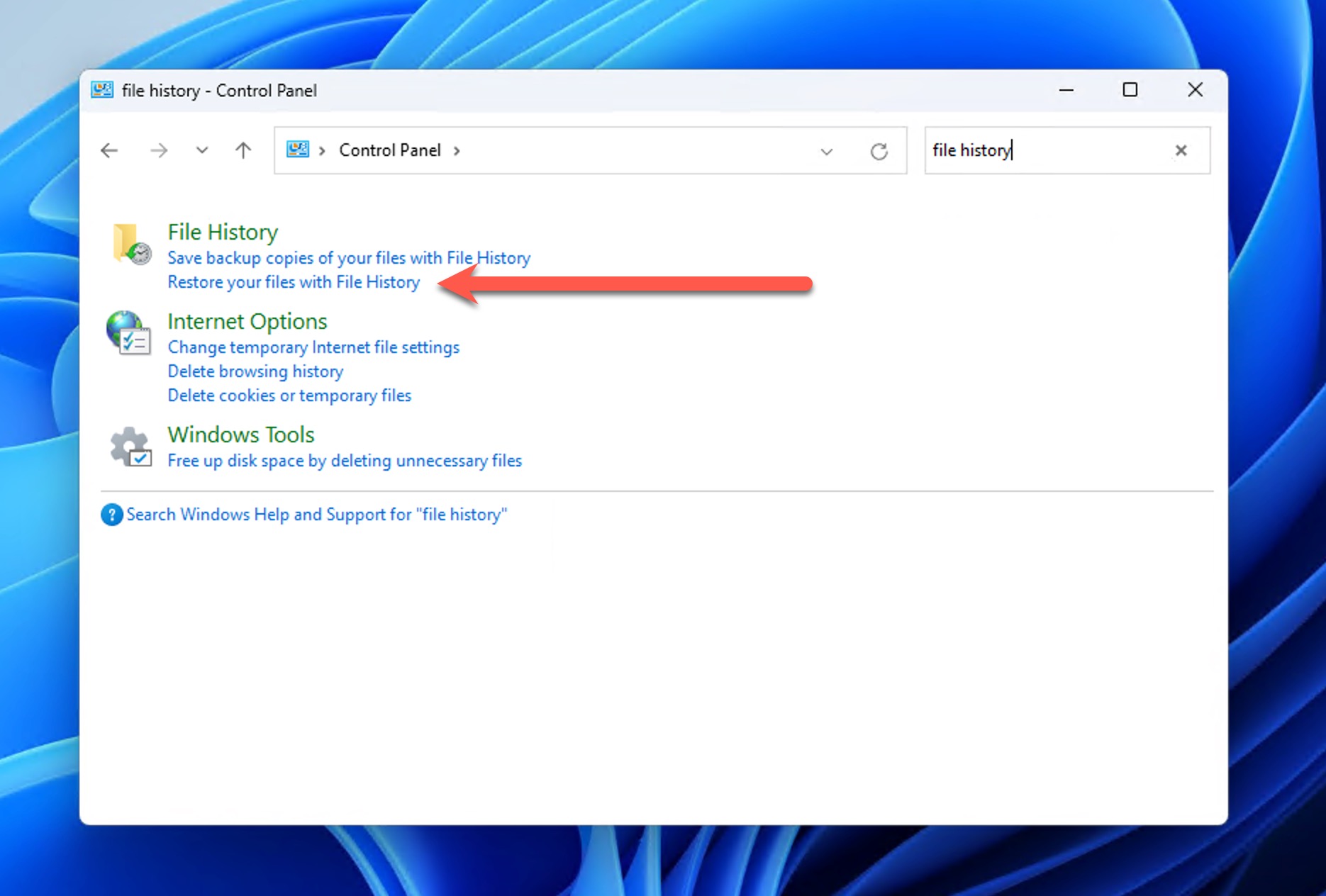
- Type “File History” in the Control Panel search box (top-right corner) and select Restore your files with File History from the results.
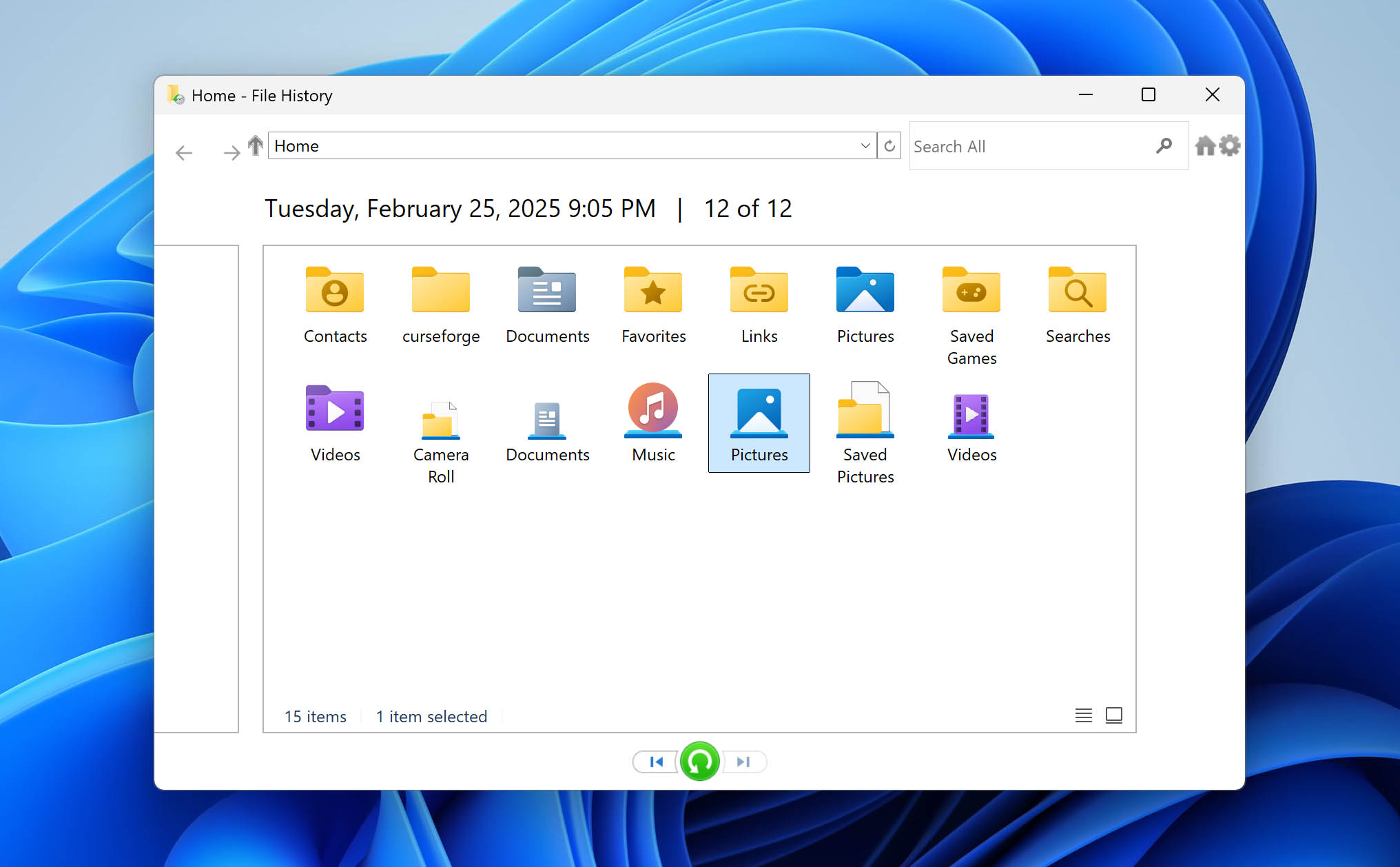
- Navigate to the location where your deleted folder was stored and use the navigation arrows at the bottom to browse through different backup dates.
- Select the folder you want to restore, and click the green restore button at the bottom of the window to recover your deleted folder on Windows.
Method 3: Recover Using the Backup and Restore Feature
Windows 10 and 11 still include the classic Backup and Restore feature that was first introduced with Windows 7, and you can use it to retrieve a deleted folder from both local and network backups.
To recover deleted folders using Backup and Restore:
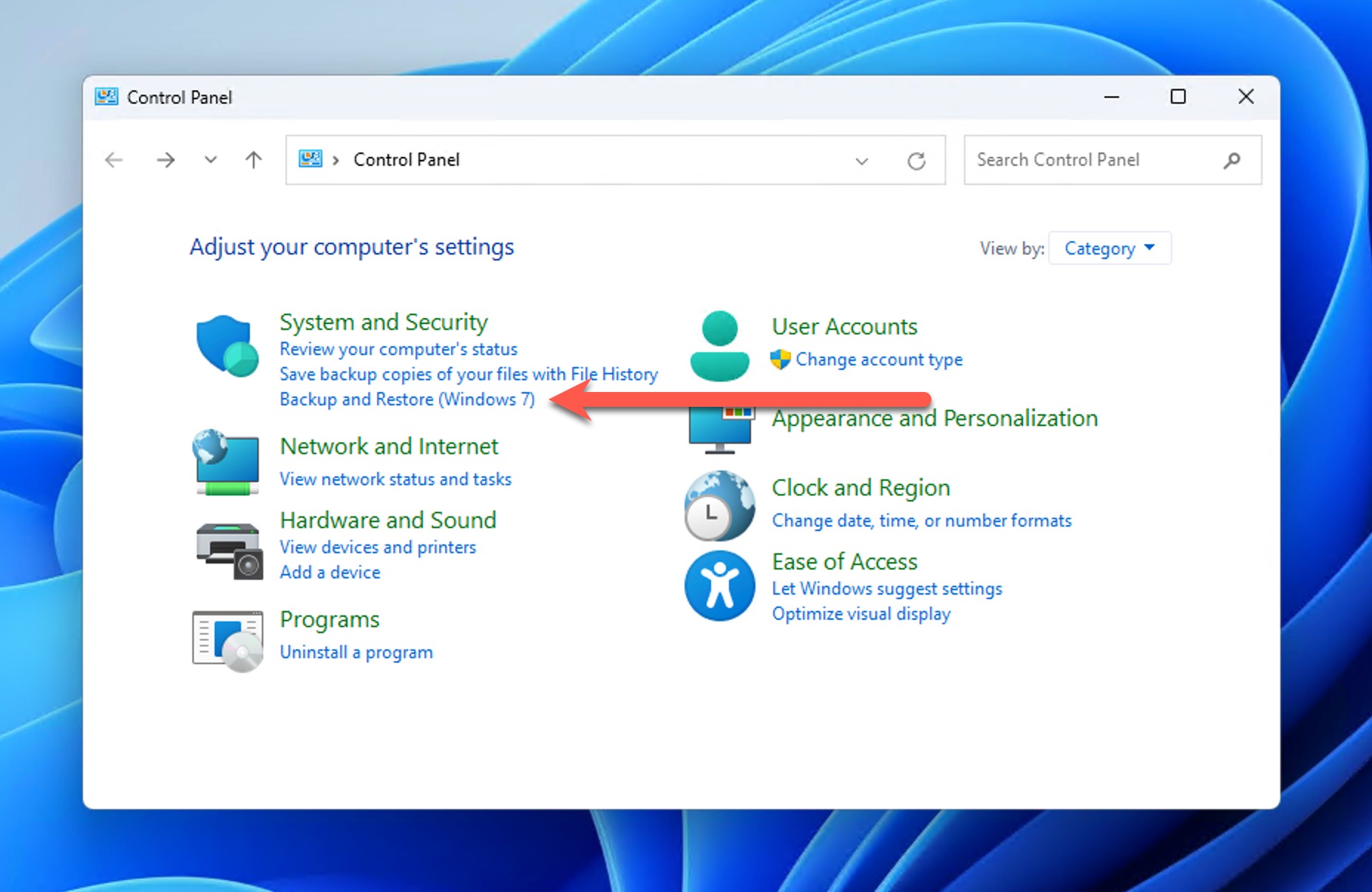
- Click the Windows Start button and type “Control Panel” in the search box. Select Control Panel from the search results.
- Navigate to System and Maintenance (or System and Security on Windows 11) > Backup and Restore.
- In the Backup and Restore window, click Restore my files if your backup is detected. If your backup isn’t automatically detected, click Select another backup to restore files from and browse to the location of your backup.
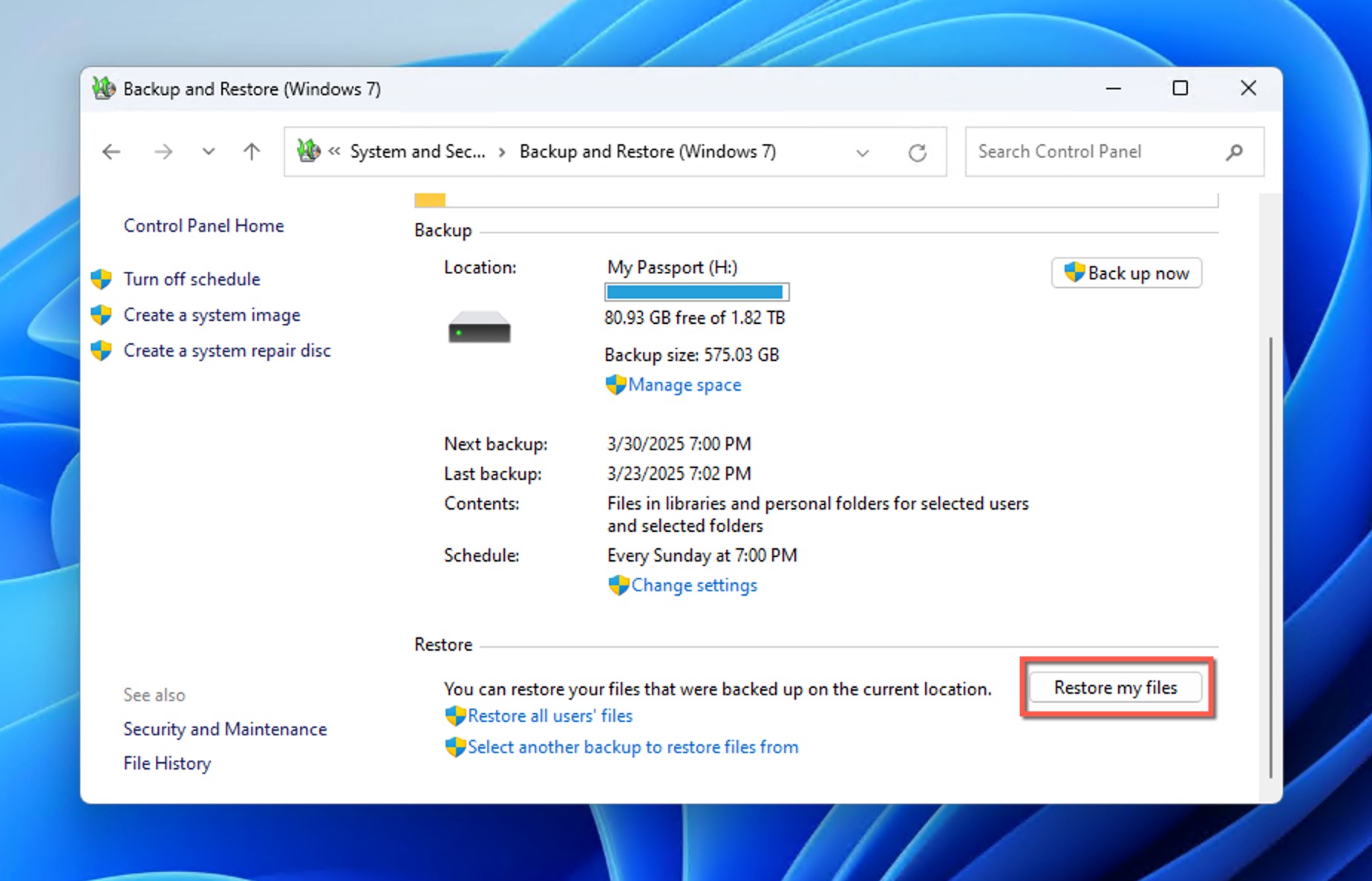
- The recovery wizard will open, allowing you to browse for specific files or folders. Select your deleted folder and choose whether to restore to the original location or a new location.
Method 4: Try the Windows File Recovery Tool
Microsoft provides its own data recovery tool for Windows, called Windows File Recovery, and you can use it to recover the content of any permanently deleted folder.
To install Windows File Recovery, you need Windows 10 2004 and above. If you meet this requirement, then you can follow these steps:
- Launch Microsoft Store and look for”Windows File Recovery” using the search bar.
- Install the Windows File Recovery tool.
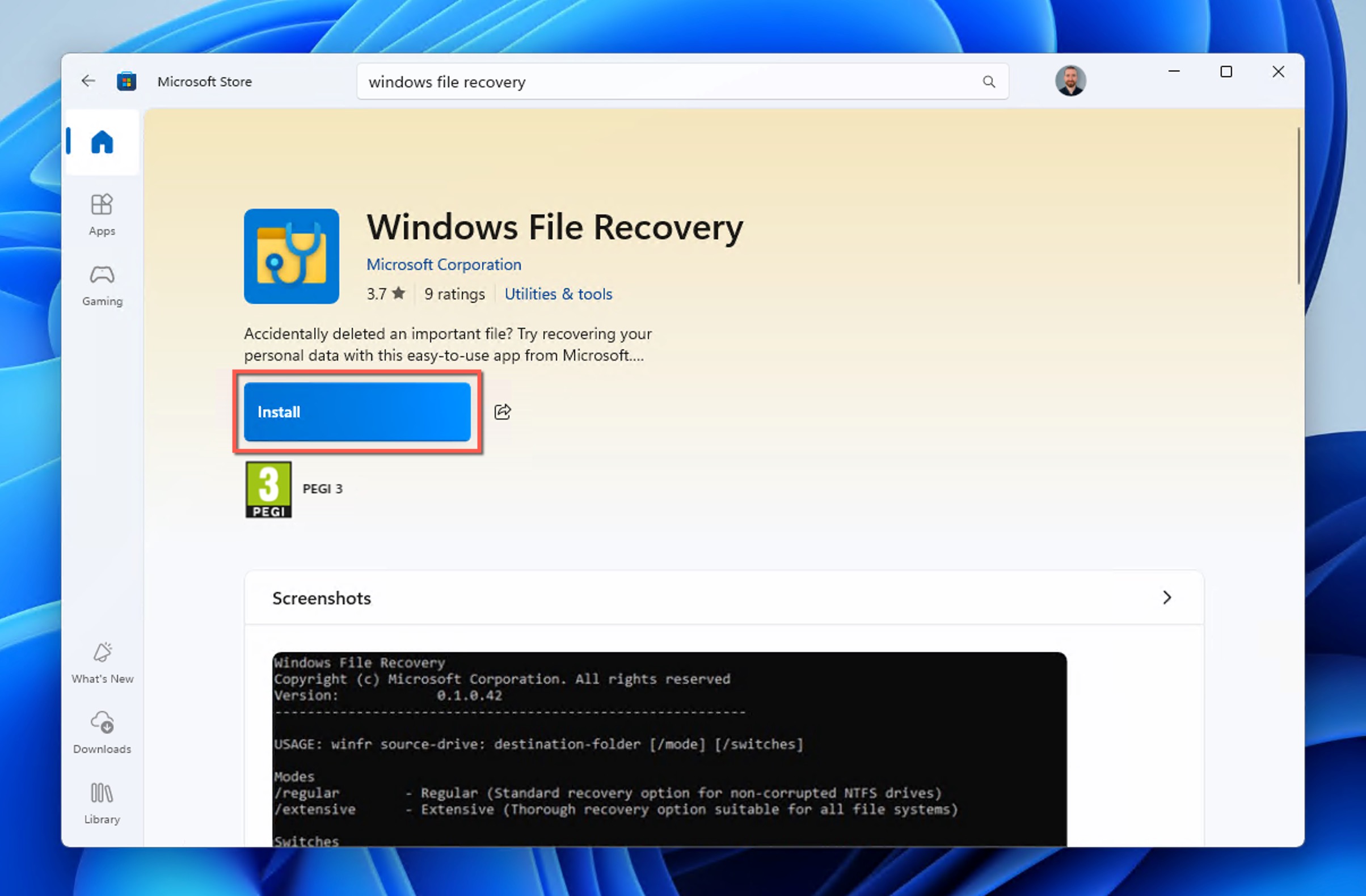
- Press the Windows key, type “Windows File Recovery” and select it from the results.
- Use the following command syntax to recover your deleted folder: winfr source-drive: destination-drive: /mode /switches
For example, here’s how you can recover a deleted Documents folder using Regular mode:
winfr C: E: /regular /n \Users\YourUsername\Documents\
This command would attempt to recover all deleted files and folders that were located in the Documents folder (under your user profile) from the C: drive, and restore them onto the D: drive. You can also recover only specific file types from a deleted folder:
winfr C: E: /regular /n \Path\To\Folder\*.docx /n \Path\To\Folder\*.pdf
The command above recovers Word documents and PDFs from a specific folder location.
Method 5: Download the Folder from OneDrive
Was the permanently deleted folder stored in the OneDrive folder on your computer (Microsoft OneDrive is integrated into Windows 10 and 11, so there’s a good chance that it was)? Then you might be able to recover it from your OneDrive cloud backup or OneDrive’s cloud Recycle Bin folder. First, check if the folder still exists in OneDrive:
- Open your web browser and go to https://onedrive.live.com/
- Sign in with your Microsoft account credentials (the same account you use on your Windows computer).

- Browse through your OneDrive files to locate the deleted folder. If it’s still visible in the cloud but not on your computer, it’s possible the deletion hasn’t synced yet.
If you find it still present in OneDrive, then you should download it to your device. If not, then also check the OneDrive cloud Recycle Bin:
- While still on the OneDrive website, look for Recycle bin in the left navigation pane.
- Locate your deleted folder. You can use the search function at the top if you have many deleted items.
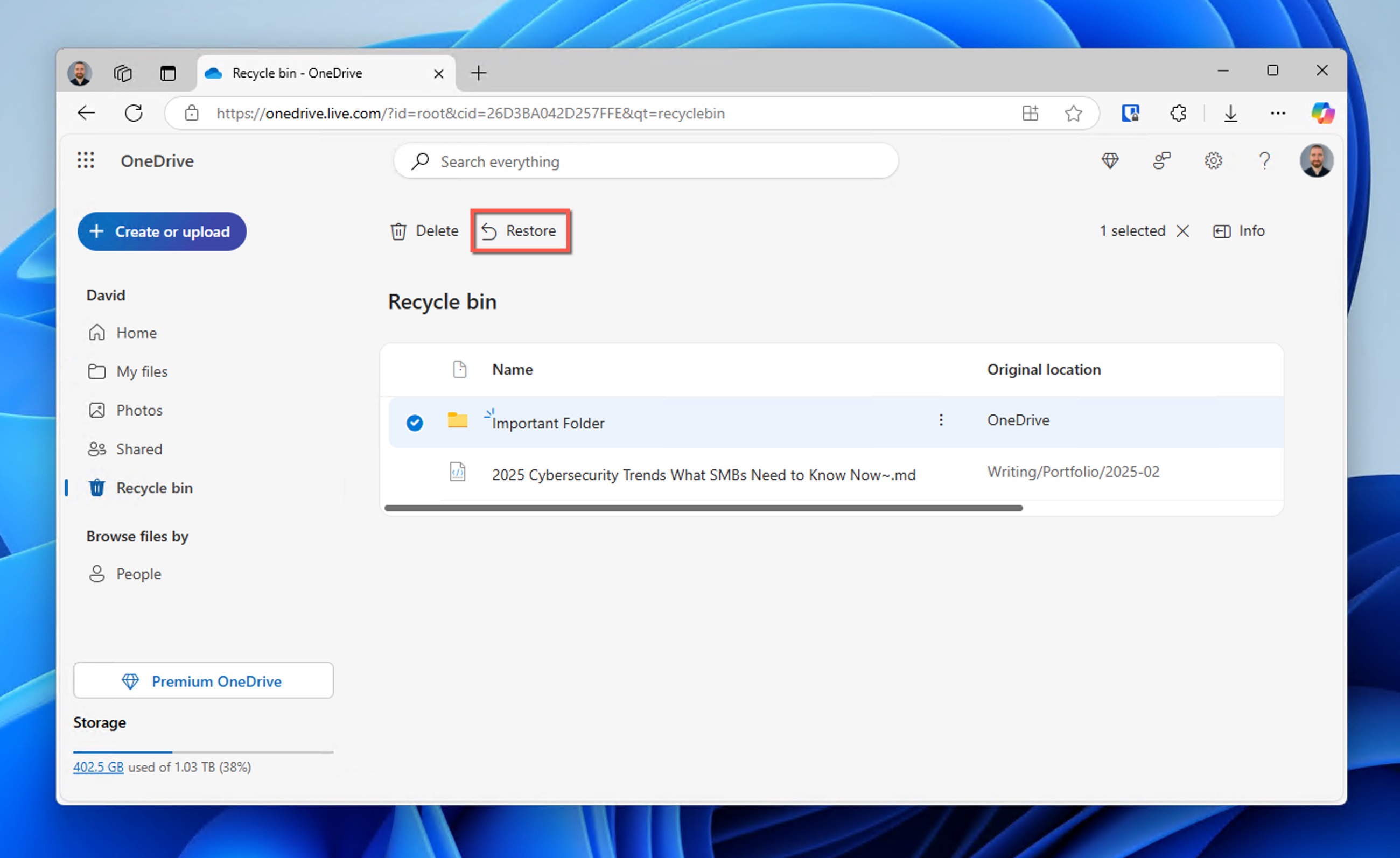
- Select the folder by clicking on it, then click the Restore button.
Once restored, the folder will automatically sync back to your computer’s OneDrive folder.
Method 6: Consider Contacting Data Recovery Professionals to Recover Your Folder

While the DIY recovery techniques described in this article are all fairly straightforward and capable of delivering great results, they aren’t your only option. You can also pay data recovery professionals to get the folder back for you.
Professional data recovery is a great choice (and often the only one) to recover the permanently deleted folder when dealing with:
- Failed recovery attempts: If you’ve tried using data recovery software but it either doesn’t find your folder or recovers corrupted versions of your files.
- Lack of technical confidence: If you’re uncomfortable performing the technical steps required for DIY recovery and don’t want to risk something going wrong.
- Physical damage: If your storage device is making unusual noises, not being recognized by your computer, or showing other signs of physical failure. Professional recovery technicians have specialized equipment to recover data from physically damaged drives in clean-room environments.
Even though professional data recovery is significantly more expensive than the DIY methods described earlier in this article, all reputable services won’t charge if they can’t recover your files, and they will provide you with an accurate price quote beforehand to prevent unpleasant surprises.
FAQ
No, your folder is not guaranteed to be lost forever. Despite the fact that using Shift+Delete bypasses the Recycle Bin and performs an immediate deletion, the actual data remains physically on your storage device until the physical storage blocks are overwritten with new data, giving you a chance to recover your folder using specialized data recovery software.
Your folder may not be in the Recycle Bin if you deleted it using Shift+Delete, if it exceeded the Recycle Bin size limit, if it was deleted from a removable drive, or if it was deleted via Command Prompt. In such situations, you can use data recovery software to directly scan the storage device from which the folder was deleted. If it still hasn’t been overwritten, then you’ll be able to recover it.
No, files deleted from USB drives and SD cards typically bypass the Recycle Bin and are deleted immediately. However, recovery is still possible using data recovery software since the data isn’t immediately erased from the drive.
System Restore only affects system files, registry settings, and installed programs. It doesn’t restore personal files or folders that have been deleted. You’ll need to a different recovery methods, such as the File History feature or data recovery software like Disk Drill.
Yes, SSDs make file recovery more challenging due to TRIM functionality, which efficiently wipes deleted data blocks to improve performance. On SSDs with TRIM enabled (most modern SSDs), permanently deleted files may be wiped within minutes or hours of deletion, which is why it’s essential to begin the recovery process as soon as possible.
You can recover permanently deleted folders on Windows without software using File History:
- Open the Start menu.
- Type “restore” and select Restore your files with File History. Navigate to the location where the folder was stored.
- Use the arrows to check older backups.
- Select the folder and click Recover.