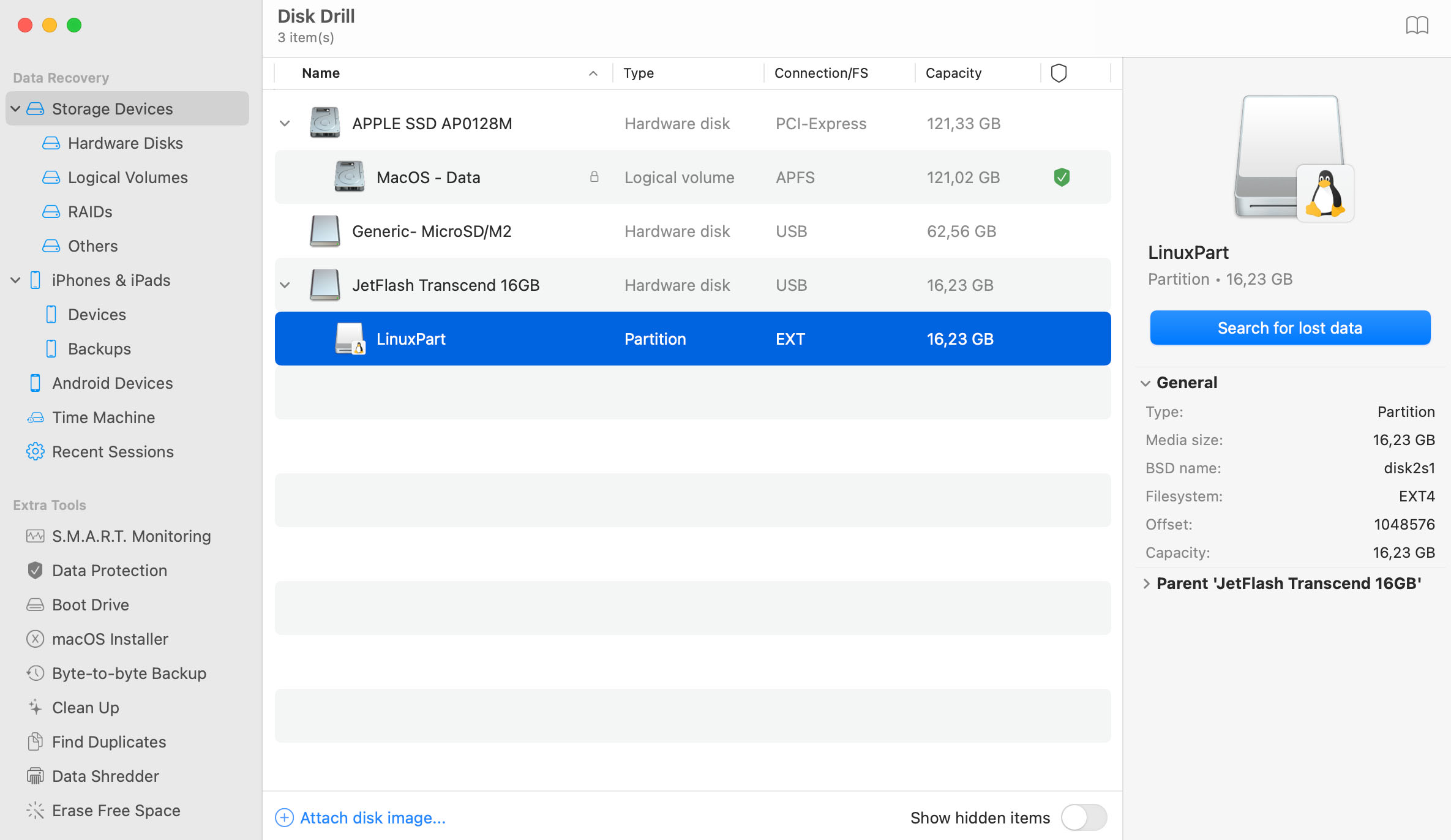
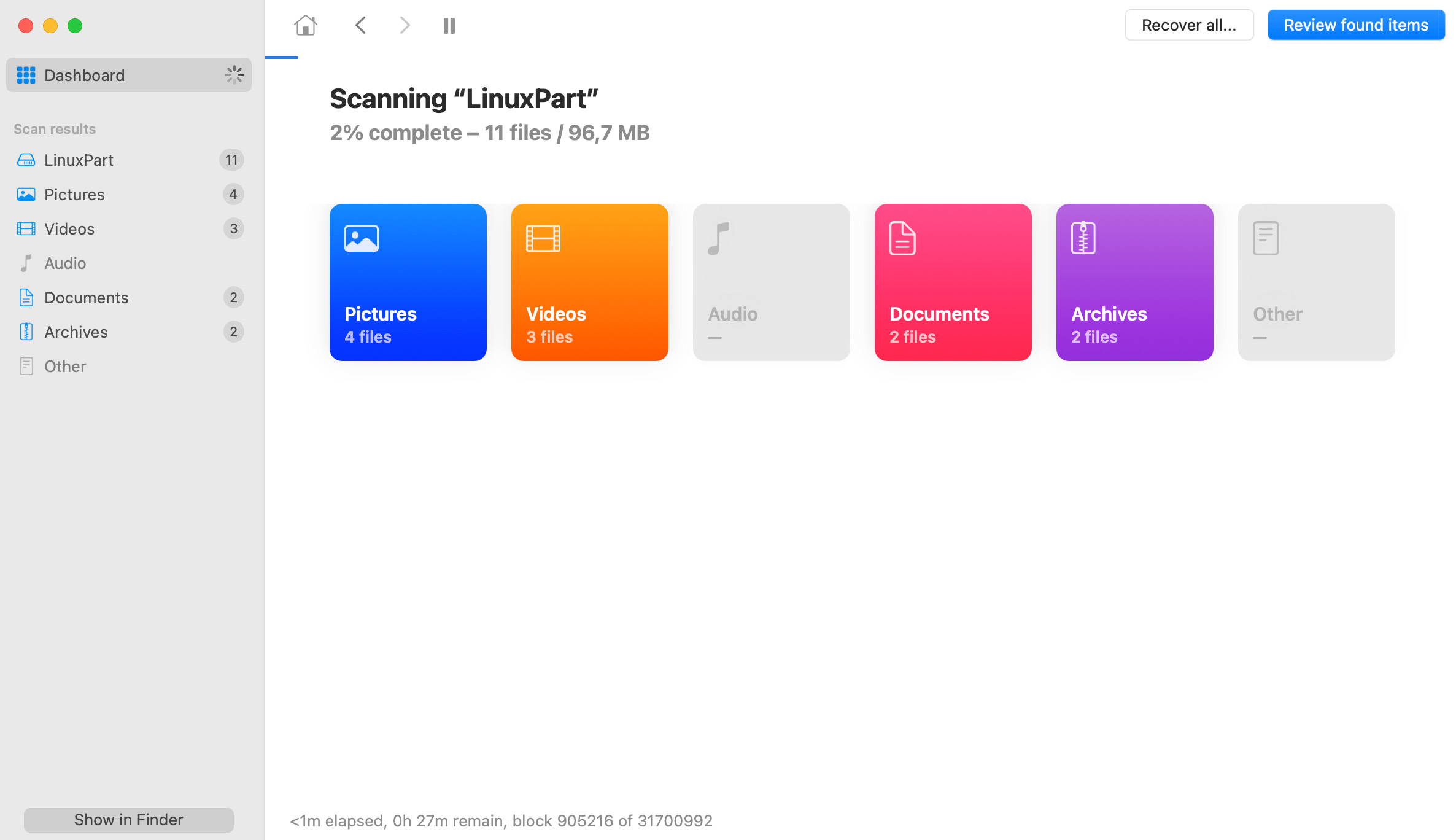
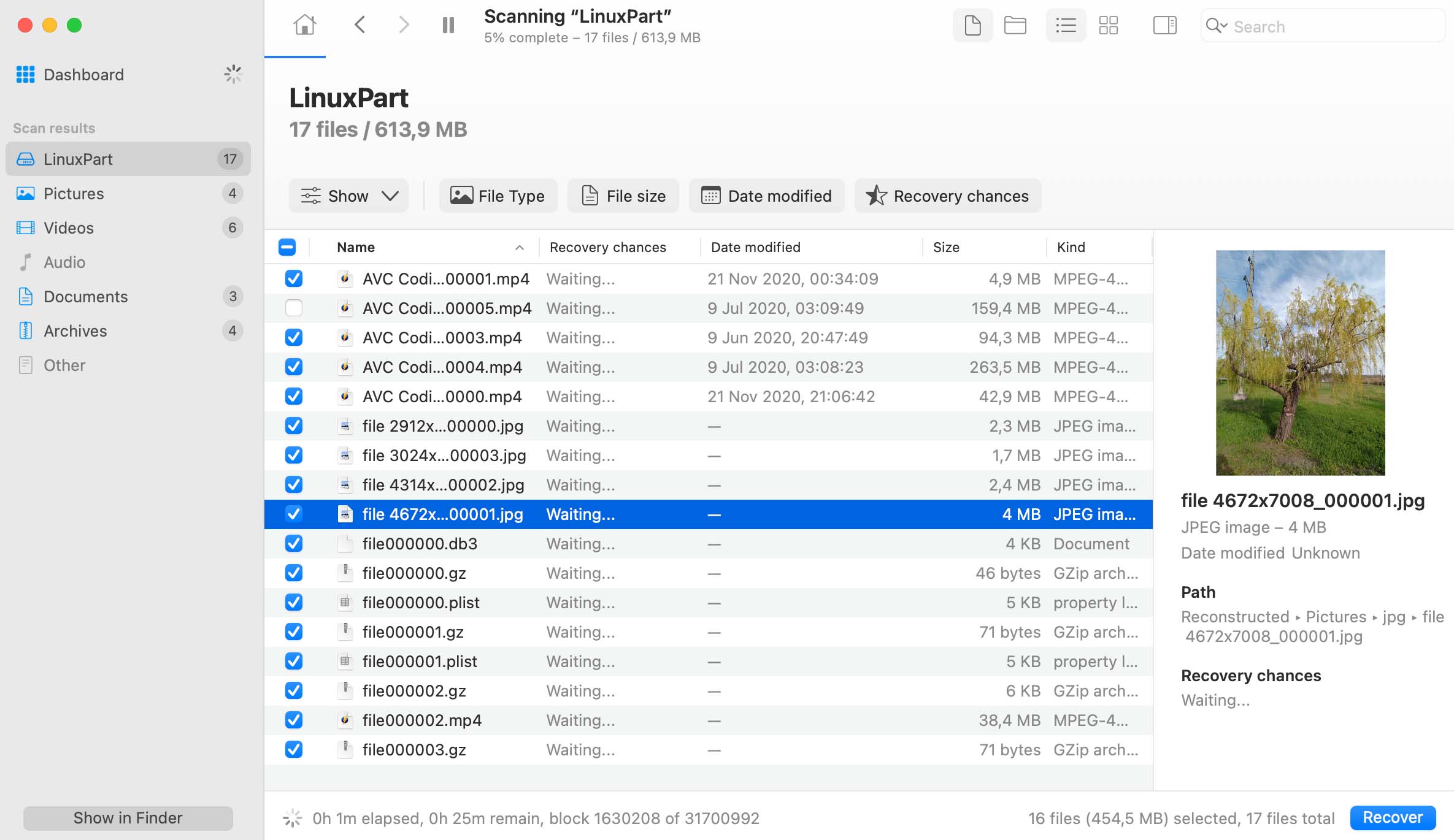
Once the scanning is over, you are ready for your Linux file recovery. Make sure you are not recovering your deleted Linux data to the same drive you were scanning, this may not only result in poor recovery quality, but may also invalidate the remaining data, as it will be overwritten. It is generally super-important to stop using your hard drive the very moment you realize there was data erased that needs to be retrieved back.
The best data recovery software applications for Linux include:
- PhotoRec (free and open source)
- R-Studio (from $49.99)
- GNU ddrescue (free and open source)